I
t is common practice for customers of fiber producers, nonwovens manufacturers and
textile finishers to demand steady product quality. Quality-conforming production of goods with
defined properties therefore requires the observation of relevant characteristics. For this
purpose, quality assurance and surveillance systems must be used. A basic requirement of these
systems, however, is the acquisition of all relevant technological parameters and technical machine
data.
In the past, test samples usually were taken during individual production stages. The test
results were available at a later date when it was no longer possible to influence running
production. Conclusions as to necessary modifications of the production parameters could be drawn
only by comparing shift reports.
However, direct monitoring of the production process lately has come to the fore, and
individual process stages can be influenced directly. Production without on-line process monitoring
would be unthinkable today.
As a result, ever more complex demands are made on measuring and testing technology, and
on-line measuring systems are required.

and monitor the production process.
On-line process monitoring allows the
acquired data to be evaluated immediately so production parameters can be influenced directly. This
results in uniform quality, high productivity and minimized raw material losses.
When looking at the production of nonwovens for technical textiles, there are four main
processes:
• fiber opening/blending;
• web formation;
• web bonding; and
• enhancement/finishing.
The first three stages are combined into a continuous process. Set-point entries for areal
weight, production speed, drafting and web structure — machine direction/cross direction ratio or
cloudiness, for example — and comparison with actual values provide the base for controlling
nonwovens production. The individual stages are connected using a process control system (PCS).
Such large data quantities can no longer be processed using conventional control techniques.
All current process data and fault messages are provided through interfaces, enabling
statistics generation with regard to failure frequency of certain machine components for quality
assurance and to do preventive maintenance work.
Process Control Systems
During the past few years, there have been enormous innovations in drive and control
engineering for textile machinery construction. The trend has gone from simple independent machine
control systems equipped with a minimum of operating and indicating elements to complex PCSs for
machines or processing lines.
This development has been necessary to meet the increasing demands made on energy
utilization, waste reduction, environmental protection, operating staff savings, fabric qualities
according to ISO 9000 standards, and production outputs for ever smaller lots.
PCSs for controlling and monitoring production processes are an integral part of all machine
control systems today. A programmable logic controller (PLC)-based machine control system in
combination with computerized instrumentation and control machine technology has become the
standard for textile machinery manufactured by Germany-based Fleissner GmbH, which has successfully
used PCSs for years.
Staple-fiber processing lines, spunlace lines for nonwovens and technical textiles,
open-width washing machines, raw wool scouring machines, carpet dyeing lines and similar complete
lines from Fleissner are always provided with a PCS. Man-to-machine communication in small lines or
individual machines mostly takes place via fully graphic operator terminals.

The following machine control systems
are used in practical operation:
• conventional control systems including relay controls and mini-PLC;
• operator terminal with PLC; and
• industrial personal computer (PC) with PCS.
Continuous production lines today are delivered with a PCS and industrial PC because of the
large amount of data that must be processed.
Modern flexible production lines require a large number of technological parameters and
provide a lot of process information. This information can only be entered and represented by means
of modern man-machine communication.
A clearly structured operating panel with simple mechanisms for operation, parameter
assignment and listing is essential for high acceptance by machine operators.
Numerous ways of representation and an integrated alert processing system enable quick and
extensive diagnostics, and thus serve to reduce machine standstills.
The degree of automation and the efficiency of modern textile machinery and man-made fiber
lines are determined mainly by the control and instrumentation system used.
Advantages Of Automatic Process Control
The fully automatic PCS developed by Fleissner is used to optimize economic
production efficiency and the quality of the fabricated products.
This PCS enables automatic calculation and optimization of all required machine parameters by
specifying technological conditions.
A fully automatic PCS provides the conditions required for quality assurance systems to
comply with ISO 9001:
• cost-efficient operation by optimizing energy consumption;
• optimum product quality by automatically establishing process parameters;
• quick and reproducible product changes by recipe management;
• easily retraceable line status representation with all required machine parameters on a
full graphics color monitor;
• monitoring of limit values for actual process values and set-point entries;
• recording of measured values in trend form and storing for long periods (line
optimization/quality control);
• password entry to avoid unauthorized access;
• possible connection to higher-order process control systems; and
• simple operation with an easy-to-understand user interface.
Complete Line Control Systems, Technical Concepts
The basic system comprises a PLC combined with an industrial PC in various
configurations. This industrial PC replaces conventional control system interfaces such as function
tables, control desks, display panels and equipment for recording and displaying data.
The number of operating elements is thus reduced to a few essential functional components.
All control information to the line and status reports from the line pass through the programmable
control(s) to the system computer.
The individual PLCs of complex line configurations are connected with the system computer by
a data bus. Regardless of the scope of required control technology, the system uses standard
hardware and software components.
The modular hardware component design optimizes circuit diagram preparation. A modular
software system for PLC and visualization is also required for efficient line control system
planning.
Basic control elements include the following:
• basic functions such as lamp test and others for general control functions;
• operating functions such as manual/automatic/inching and others;
• fault detection and evaluation for auxiliary equipment including emergency stops and
voltage control;
• detection/monitoring of technological functions including infrared (IR) limit switches;
• set-point generation for transport drives;
• set-point generation for temperature control loops and software controller blocks;
• modules for IR exhaust air flaps position selection and detection;
• modules for linking visualization components in the operator terminal; and
• drive coupling through analog signals or bus systems.
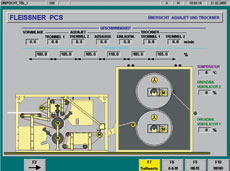
parameters including production information, among other data.
Basic modular design concepts also
are found in the structure of the visualization program. Based on a fixed framework structure, the
following individual technological features are incorporated in the PCS system:
• menu for selecting the desired submenu;
• line/machine overview with essential machine parameters;
• system overview display of machine including production information, rates and downtimes;
• recipe management;
• log management;
• alert and message overviews;
• entry listings of parameter changes;
• trend displays;
• graphic overview displays of temperatures and pressures;
• entry screens for set points; and
• service screens for machine settings such as controller parameter assignment and entry of
basic set points.
Recipe management usually is included when using a PCS. Product-specific recipes that can be
selected by product names are used to store all relevant setting data for the process. When
changing products, the complete data set of all set-point parameters can be transmitted to the PLC
simply by selecting the respective recipe name, ensuring short changeover times for product changes
and high reproducibility of technological data.
Operation
Individual operators are assigned passwords for different access authorization levels, allowing
them to change parameter values, operating modes, listing functions and other parameters. Functions
not enabled on the respective access level are not displayed in the screen menu, thus facilitating
operation and improving safety.
All PLCs can be provided with an optional serial interface that links them to other
computers. All current process data, status and alert indications are provided through this
interface.
Apart from hardware and software for quality control, startup and maintenance service also is
essential to a quality assurance system. It is becoming increasingly common to connect the
customer’s PCS to the machinery manufacturer via a modem to ensure a quick solution by remote
diagnosis in the event of a malfunction. Experienced electrical specialists therefore are able to
attend to the customer throughout the process from order placement to machine delivery. This is a
prerequisite for optimum service and safe, reliable production conditions.
Editors Note: Alfred Watzl is director, sales and marketing, Fleissner GmbH.
March/April 2006




