By Jim Phillips, Yarn Market Editor
By Jim Phillips, Yarn Market Editor
After a string of months in which demand for U.S-made yarns remained remarkably high, especially considering inflation rates and a slowing economy, the past few weeks have seen a slight-to-moderate drop in inquiries and orders for a number of spinners.
“I think we’re in a lull — a temporary one, I hope — because the market is currently saturated,” said one source. Added another, “The retail pipeline looks to be full at the moment. Store shelves are generally well stocked, and our customers are hesitant to place new orders until they see how the economy goes. Fingers are crossed at this point that we can avoid a recession, but the odds of that seem to be decreasing day by day. Consumers have already begun to tighten up their pocketbooks.”
In fact, The Expectations Index, part of the Consumer Confidence Index published by The Conference Board®, although recovered slightly in August from July’s nine-year low, still remains below a reading of 80, suggesting recession risks continue. Consumer concern about inflation remains elevated, but has retreated from the high of previous months.
Cotton Prices, Sustainability Practices
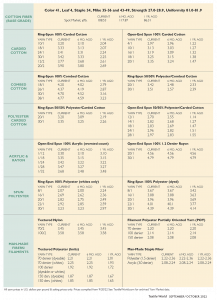
Spot quotations for the base quality of cotton (color 41, leaf 4, staple 34, mike 35-36 and 43-49, strength 27.0-28.9, and uniformity 81.0-81.9) in the seven designated markets measured by the USDA averaged 108.53 cents per pound for the week ending September 15, 2022. The weekly average was up from 90.71 cents reported for the corresponding period a year ago. Daily average quotations ranged from a high of 111.07 cents Monday, September 12 to a low of 106.10 cents Thursday, September 15. Spot transactions reported in the Daily Spot Cotton Quotations for the week ended September 15 totaled 7,467 bales. This compares to 7,613 spot transactions reported the corresponding week a year ago. Total spot transactions for the season were 20,447 bales compared to 24,772 bales during the same period a year ago.
The ICE October settlement price ended the week at 105.24 cents.
In other cotton news, Cotton Incorporated, as part of the USDA Partnership for Climate-Smart Commodities pilot project, is collaborating with industry leaders to focus on increasing the adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices. The project will build markets for climate-smart cotton and provide technical and financial assistance to more than 1,000 U.S. cotton farmers to advance adoption of climate-smart practices on more than one million acres. This will allow the production of more than four million bales of climate-smart cotton over five years.
“The climate-smart cotton program brings together USDA with private industry resources to increase the production and demand for climate-smart cotton that will help the U.S. cotton industry meet the ten-year sustainability goals,” noted Dr. Jesse Daystar, vice president and chief sustainability officer for Cotton Incorporated.
Eastman, Patagonia® Collaborate On T-shirts
Eastman, maker of Naia™ Renew sustainable fibers and yarns, is collaborating with Patagonia® to offer a limited run of T-shirts made with Naia Renew ES — Eastman’s latest fiber offering made with increased recycled content.
Named for its enhanced sustainability, Naia Renew ES is made with 60 percent recycled content. Unlike other cellulose-based yarns and fibers, this option requires fewer virgin materials to make an environmentally friendly product. Naia Renew ES is made from a combination of 40 percent molecularly recycled waste material, 20 percent recycled cellulose, and 40 percent renewable wood pulp.
The 20 percent recycled cellulose comes from waste materials, textiles waste and non-forest-derived cellulose waste. This innovation is made possible through Eastman’s continuous efforts to collaborate with eco-conscious partners throughout the value chain. For example, the Naia team has partnered with GP Cellulose, a pulp supplier with a focus on sustainability, to integrate renewable forest fibers and non-forest fiber solutions into its feedstock.
The remaining 40 percent recycled content comes from Eastman’s molecular recycling technology that breaks down hard-to-recycle waste materials like plastic packaging and old carpet into fundamental building blocks to produce the acetic acid used to make cellulose acetate yarn and fiber.
September/October 2022